Advanced material handling innovation is the hallmark of our engineering team. Expert knowledge that’s constantly evolving with the pulse of the industry’s trends ensures our team is fluent with the latest technology. With experts in the fields of controls engineering, mechanical engineering, design engineering and project management, your project is developed to the most technical capacity.
Autodesk Vault, AutoCAD, and Factory Design Suite provide our engineering team with diverse technologies to formulate customer specific material handling solutions. These sustainable solutions foster customer relationships that focus on our primary values: quality, trust, and overall project integrity.
DMW’s on site engineering lab provides a unique space for the research and development of new material handling technologies. These developments provide our customers with access to the latest innovations in material handling. Utilizing 3D printing technology, our team research and test new design and reverse engineering concepts. Utilizing various field tests, process improvements and project efficiencies can be offered to our customers through the development of new parts and mechanisms that innovate the material handling process.


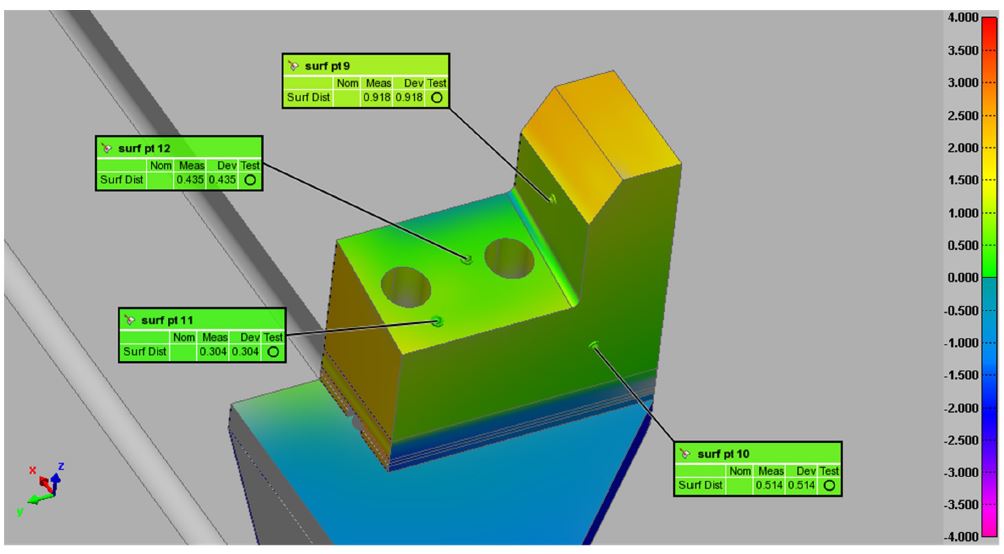
Engineering services we provide include:
- New Product Development
- Customer Specific Research and Development
- Prototyping
- 3D Capabilities
- Predictive Engineering and Design Capabilities:
- Chain Pulls
- FEA (Finite Elemental Analysis)
- DFMEA (Design Failure Mode Effect Analysis)
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines)
- PLC Programming and Controls
